Title: Understanding Coronavirus Pink Eye: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention
Introduction
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the medical community has uncovered a myriad of symptoms associated with the novel coronavirus. Among these symptoms is the lesser-known but significant occurrence of conjunctivitis, colloquially known as "pink eye." This ocular manifestation has prompted researchers and healthcare professionals to delve deeper into its causes, symptoms, and potential links to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. This article aims to shed light on the phenomenon of coronavirus pink eye, its symptoms, causes, and preventive measures.
Coronavirus Pink Eye: An Overview
Conjunctivitis, commonly referred to as pink eye, is the inflammation of the conjunctiva—the thin, transparent layer of tissue that covers the front surface of the eye and lines the inside of the eyelids. This condition leads to redness, discomfort, and, in some cases, discharge from the eyes. There are several types of conjunctivitis, including viral, bacterial, allergic, and irritant conjunctivitis. Viral conjunctivitis, as the name suggests, is caused by viruses and is highly contagious.
In recent times, an intriguing connection has emerged between the SARS-CoV-2 virus and conjunctivitis. Reports of coronavirus patients experiencing pink eye symptoms have raised questions about the possible transmission of the virus through ocular secretions and the mechanisms behind this occurrence.
Symptoms of Coronavirus Pink Eye
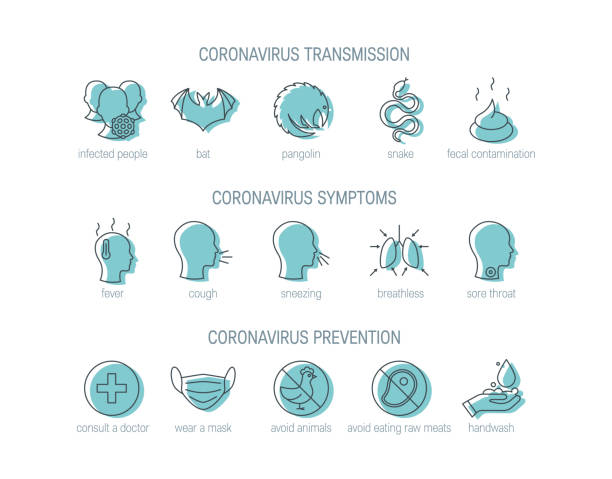
Coronavirus pink eye shares several common symptoms with other forms of conjunctivitis, making it essential to differentiate them for accurate diagnosis. The hallmark symptoms of coronavirus pink eye include:
Notably, some individuals infected with the coronavirus may experience conjunctivitis as the sole symptom or one of the early symptoms, even before the respiratory symptoms manifest.
Causes and Mechanisms
The relationship between SARS-CoV-2 and pink eye is still being explored, but it's believed that the virus can cause conjunctivitis through direct contact with the eyes. The virus gains access through respiratory droplets or by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus and subsequently touching the eyes. Once the virus enters the conjunctival tissue, it triggers an inflammatory response, leading to the characteristic redness and discomfort associated with pink eye.
While SARS-CoV-2 RNA has been detected in tears and conjunctival samples of some infected individuals, more research is needed to determine the extent to which the virus can be transmitted through ocular secretions. It's worth noting that pink eye is not a prominent symptom of COVID-19 and occurs in a relatively small percentage of cases.
Preventive Measures
To minimize the risk of contracting or spreading coronavirus pink eye, individuals are encouraged to follow the same preventive measures recommended for COVID-19:
Conclusion
As researchers continue to investigate the various aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic, the relationship between the SARS-CoV-2 virus and conjunctivitis remains an area of interest. Coronavirus pink eye, though relatively uncommon, underscores the complexity of the virus's effects on different parts of the body. By staying informed about its symptoms, causes, and preventive measures, individuals can contribute to limiting the spread of both COVID-19 and its ocular manifestations. If you experience persistent eye redness, discomfort, or any concerning symptoms, seeking medical attention is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate care.
Introduction
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the medical community has uncovered a myriad of symptoms associated with the novel coronavirus. Among these symptoms is the lesser-known but significant occurrence of conjunctivitis, colloquially known as "pink eye." This ocular manifestation has prompted researchers and healthcare professionals to delve deeper into its causes, symptoms, and potential links to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. This article aims to shed light on the phenomenon of coronavirus pink eye, its symptoms, causes, and preventive measures.
Coronavirus Pink Eye: An Overview
Conjunctivitis, commonly referred to as pink eye, is the inflammation of the conjunctiva—the thin, transparent layer of tissue that covers the front surface of the eye and lines the inside of the eyelids. This condition leads to redness, discomfort, and, in some cases, discharge from the eyes. There are several types of conjunctivitis, including viral, bacterial, allergic, and irritant conjunctivitis. Viral conjunctivitis, as the name suggests, is caused by viruses and is highly contagious.
In recent times, an intriguing connection has emerged between the SARS-CoV-2 virus and conjunctivitis. Reports of coronavirus patients experiencing pink eye symptoms have raised questions about the possible transmission of the virus through ocular secretions and the mechanisms behind this occurrence.
Symptoms of Coronavirus Pink Eye
Coronavirus pink eye shares several common symptoms with other forms of conjunctivitis, making it essential to differentiate them for accurate diagnosis. The hallmark symptoms of coronavirus pink eye include:
- Redness: The whites of the eyes become noticeably red or bloodshot.
- Watery Discharge: Increased tearing and watery discharge from the eyes.
- Foreign Body Sensation: A feeling of something gritty or foreign in the eye.
- Itching: Intense itching and discomfort in and around the eyes.
- Swelling: Eyelids may become puffy and swollen.
Notably, some individuals infected with the coronavirus may experience conjunctivitis as the sole symptom or one of the early symptoms, even before the respiratory symptoms manifest.
Causes and Mechanisms
The relationship between SARS-CoV-2 and pink eye is still being explored, but it's believed that the virus can cause conjunctivitis through direct contact with the eyes. The virus gains access through respiratory droplets or by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus and subsequently touching the eyes. Once the virus enters the conjunctival tissue, it triggers an inflammatory response, leading to the characteristic redness and discomfort associated with pink eye.
While SARS-CoV-2 RNA has been detected in tears and conjunctival samples of some infected individuals, more research is needed to determine the extent to which the virus can be transmitted through ocular secretions. It's worth noting that pink eye is not a prominent symptom of COVID-19 and occurs in a relatively small percentage of cases.
Preventive Measures
To minimize the risk of contracting or spreading coronavirus pink eye, individuals are encouraged to follow the same preventive measures recommended for COVID-19:
- Frequent Hand Washing: Regularly wash hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Avoid Touching Face: Refrain from touching the face, especially the eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Wear Face Masks: Use face masks, particularly in crowded or public spaces.
- Social Distancing: Maintain a safe distance from others, especially if they show symptoms.
- Disinfect Surfaces: Clean and disinfect commonly touched surfaces regularly.
- Eye Protection: If you're caring for a COVID-19 patient, consider wearing protective eyewear to prevent possible virus transmission through the eyes.
Conclusion
As researchers continue to investigate the various aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic, the relationship between the SARS-CoV-2 virus and conjunctivitis remains an area of interest. Coronavirus pink eye, though relatively uncommon, underscores the complexity of the virus's effects on different parts of the body. By staying informed about its symptoms, causes, and preventive measures, individuals can contribute to limiting the spread of both COVID-19 and its ocular manifestations. If you experience persistent eye redness, discomfort, or any concerning symptoms, seeking medical attention is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate care.